Preschool Science Topics & Activities for the Year!
Preschool science is all about exploration, sensory play, and hands-on discovery! Young learners are naturally curious, and this is the perfect time to introduce basic scientific concepts in a fun, engaging way. Through play, observation, and simple experiments, preschoolers develop early problem-solving and critical-thinking skills.
Below, you’ll find a breakdown of key preschool science topics by season and a list of 20+ hands-on activities to support learning all year long!
💡Check out the Libraries for printables or use the search bar.
Fall Science (Sep- Nov)
- The 5 Senses – Exploring how we see, hear, smell, taste, and touch
- Living vs. Non-Living Things – Identifying what is alive and what is not
- Weather & Seasonal Changes – Observing how fall brings changes in nature
- Pumpkins, Apples & Leaves – Exploring fall harvest and plant life cycles
Fall Science Activities:
- Leaf Color Sorting – Collect leaves and match them by color
- Pumpkin Exploration – Open a pumpkin and explore its seeds, texture, and smell
- Apple Sink or Float Experiment – Test whether apples sink or float in water
- Sensory Nature Walk – Listen for sounds, feel textures, and smell different fall scents
- Cloud in a Jar – Use shaving cream and water to create a rain cloud experiment
Winter Science (Dec- Feb)
- Day & Night – Understanding light and dark differences
- States of Matter – Exploring solids (ice), liquids (water), and gases (steam)
- Animals in Winter – How animals hibernate, migrate, or adapt
- Hot & Cold Experiments – Learning about temperature changes
Winter Science Activities:
- Melting Ice Cube Race – Test how fast ice melts with salt vs. warm water
- Shadow Puppets – Explore how light creates shadows
- Blubber Experiment – Use shortening in a bag to show how animals stay warm in the cold
- Frozen Bubbles Experiment – Blow bubbles outside in freezing temperatures and watch them freeze
- Snowflake Symmetry Art – Create paper snowflakes and discuss their unique patterns
Spring Science (Mar- May)
- Plant Growth & Gardening – What plants need to grow
- Baby Animals & Life Cycles – Learning about chicks, frogs, and butterflies
- Rain & Water Cycle – Where does rain come from?
- Sun & Shadows – How light creates shadows and moves throughout the day
Spring Science Activities:
- Planting Seeds in a Cup – Watch seeds sprout roots and leaves
- Butterfly Life Cycle Craft – Use pasta shapes to show different stages of a butterfly
- Rain in a Jar Experiment – Simulate the water cycle using warm water and ice
- Shadow Tracing with Chalk – Trace objects’ shadows outside at different times of the day
- Worm Discovery Dig – Observe worms in soil and discuss their role in nature
Summer Science (Jun- Aug)
- Water Play & Sensory Exploration – Learning through splashing and pouring
- Ocean & Beach Science – Discovering sea creatures and waves
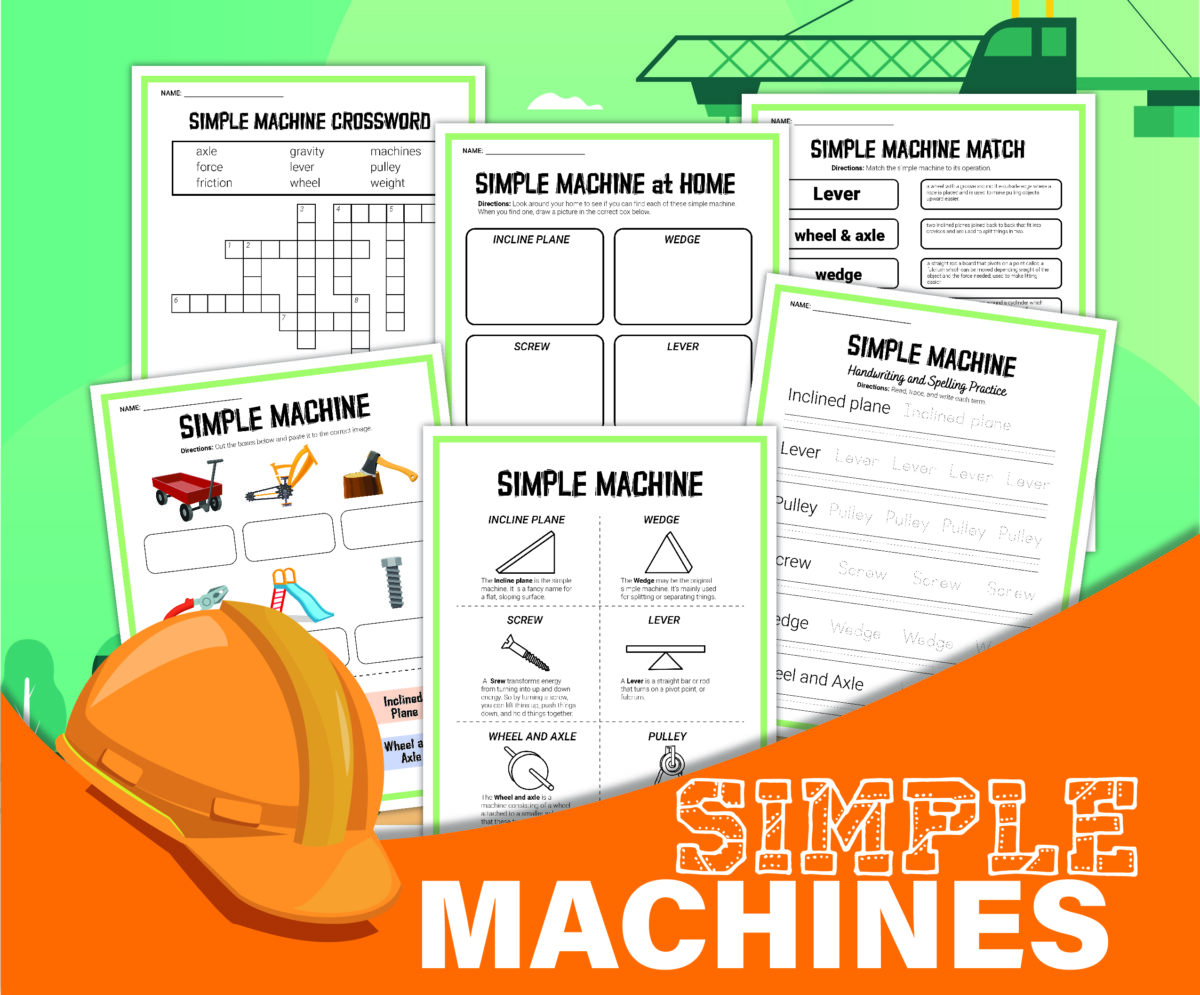
- Simple Machines for Play – Exploring ramps, wheels, and pulleys
- Sun & Heat – Understanding how the sun warms things up
Summer Science Activities:
- Sink or Float Water Play – Test different objects in a water bin
- Beach Sensory Bin – Explore shells, sand, and water in a hands-on sensory setup
- Rolling Cars Down Ramps – Experiment with how objects roll on different surfaces
- Melting Ice Science – Freeze small toys in ice and let kids experiment with melting techniques
- Homemade Bubble Solution – Mix soap and water to create giant bubbles
How to Use These Science Activities
- Encourage hands-on exploration – Let kids touch, feel, and observe
- Use simple, safe materials – Everyday items make great science tools
- Ask open-ended questions – “What do you think will happen?” or “What do you notice?”
- Let kids make discoveries – Science is about play and learning through experience